Consumers are increasingly demanding companies act responsibly towards society, their employees and their shareholders, and sustainably when it comes to the environment. Here we tell you why ESG standards are pivotal to production.
Consumers are no longer basing their purchasing decisions on price, usefulness, shelf life and other product and service features. Before splashing out, we now want to know more about the manufacturer, their way of working, where they source material, the impact of their operations on the environment and society, and other information.
More companies are making their operations sustainable through environmental, social and governance (ESG) standards to comply with laws, leverage new business models and adapt to ongoing changes in consumer demands.
Following ESG standards is a way of doing business that goes beyond success and profitability by incorporating environmental well-being in companies’ strategy.
- The “E” (environmental) means the direct and indirect impact a company has on the environment (calculated using its carbon footprint and other metrics) and the action it is taking to lessen such impact, cease harmful operations and have a positive effect on its surroundings.
- The “S” (social) means companies’ relationship with the communities they serve and how their operations can bring such benefits as employment (and championing employees’ rights), better quality of life, inclusion and human rights.
- The “G” (governance) means companies’ transparency, the composition of their board of directors, their management, their data protection practices, their values and their culture.
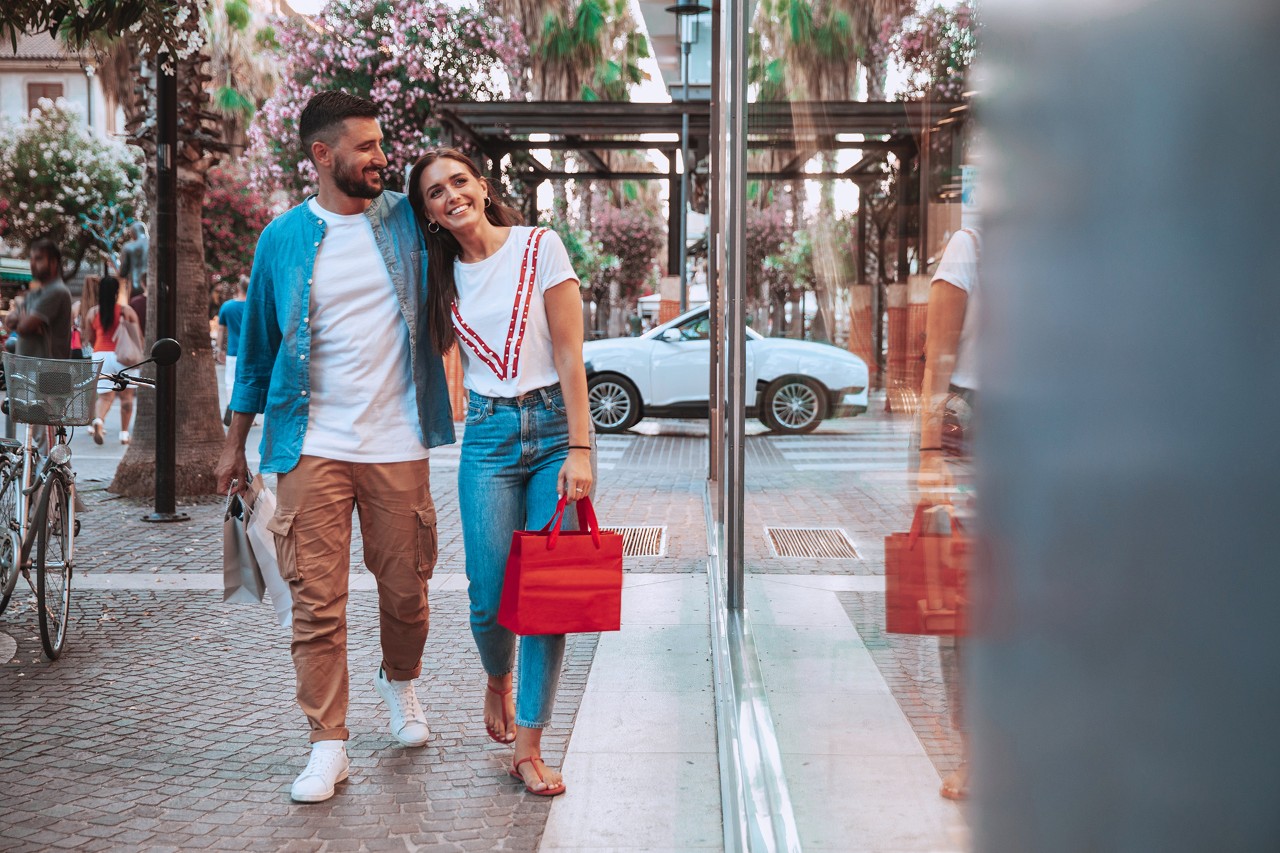

Who benefits from ESG standards?
The purpose of ESG standards is to benefit everyone who forms part of the value chain. Each party represents a link in the chain and adds value to the product or service by enhancing or adding new features until it's ready for customers to buy.
For instance, Ana is looking for a birthday present for her son and has whittled her search down to two pairs of trainers. Since they’re quite similar, she wants to find out everything she can before choosing one.
Because her son has taken an interest in sustainability and protecting the environment, the first thing she checks is the material. The manufacturer of option A uses recycled materials for the soles and synthetic, biodegradable materials for the upper part of the shoes. Thus, it doesn’t waste valuable natural resources. The manufacturer of option B uses very few recycled materials to replace rubber, plastic, textiles and other oil-based consumables that contribute to climate change.
Option A manufacturer’s production plant is close to Ana’s city. It employs people from the local area and its proximity means less CO2 emissions from transporting the trainers than the other manufacturer, which imports its products by plane from another country.
Also, Ana found out online that the manufacturer of option A sponsors a fashion and shoemaking internship programme. Having compared all the information she had on the brands, she chose option A. In addition to liking the product, it met her other expectations regarding sustainability in the value chain.
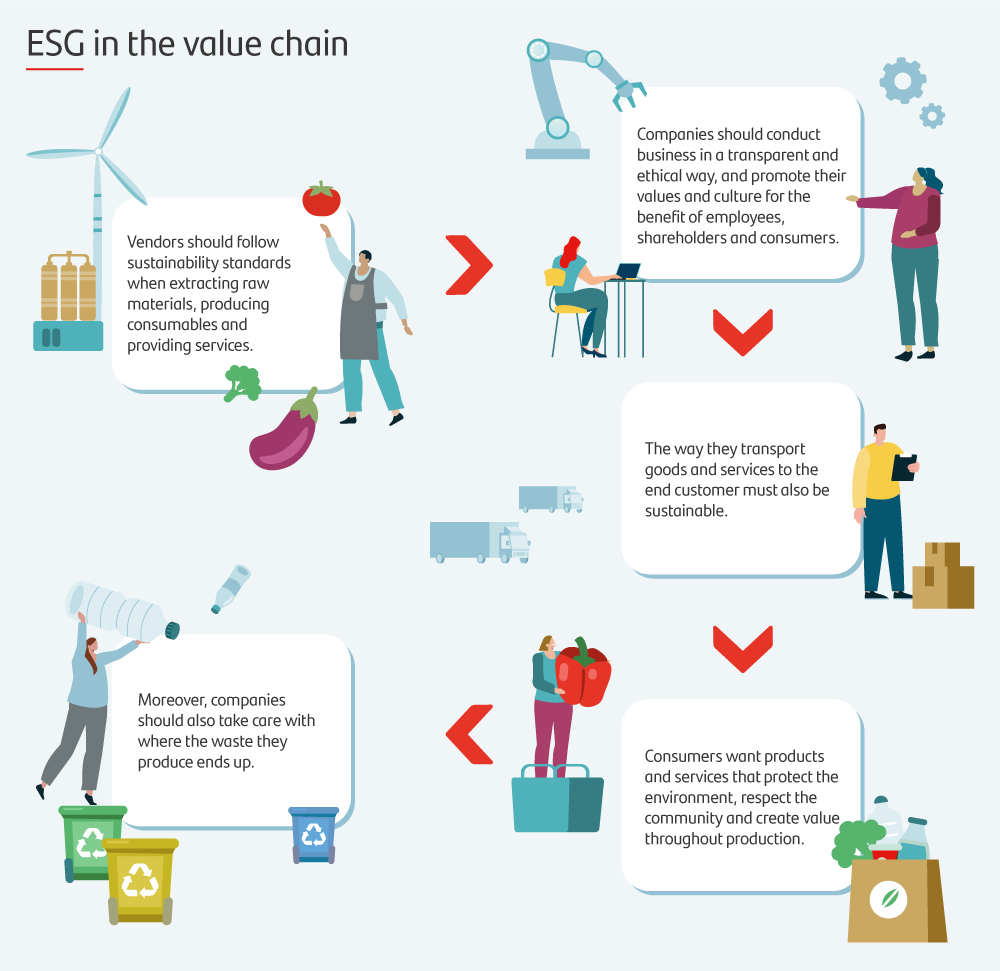
Benefits of applying ESG standards in the value chain
Companies in every industry seek feedback from their customers about their operations, as well as about their vendors, strategic partners, shareholders and investors, and other parties in the value chain. That’s why it’s important companies follow sustainability standards. If they don’t know how their vendors operate, they run the risk of reputational damage if one is found to be breaching human rights or has a high carbon footprint.
In addition to protecting a company’s reputation, making sure the entire value chain follows ESG standards makes for better use of natural resources; employees that are more motivated, committed and productive; strong corporate values; and other benefits that consumers like Ana consider when choosing between brands.
If you want to learn more, check out this piece (in Spanish) by Finanzas para Mortales (Finance for Mortals) on the link between finance and climate change and why ESG standards are crucial to meeting the United Nations’ Agenda 2030 goals.